Environment
Management and Handling of Chemical Substances
Management System
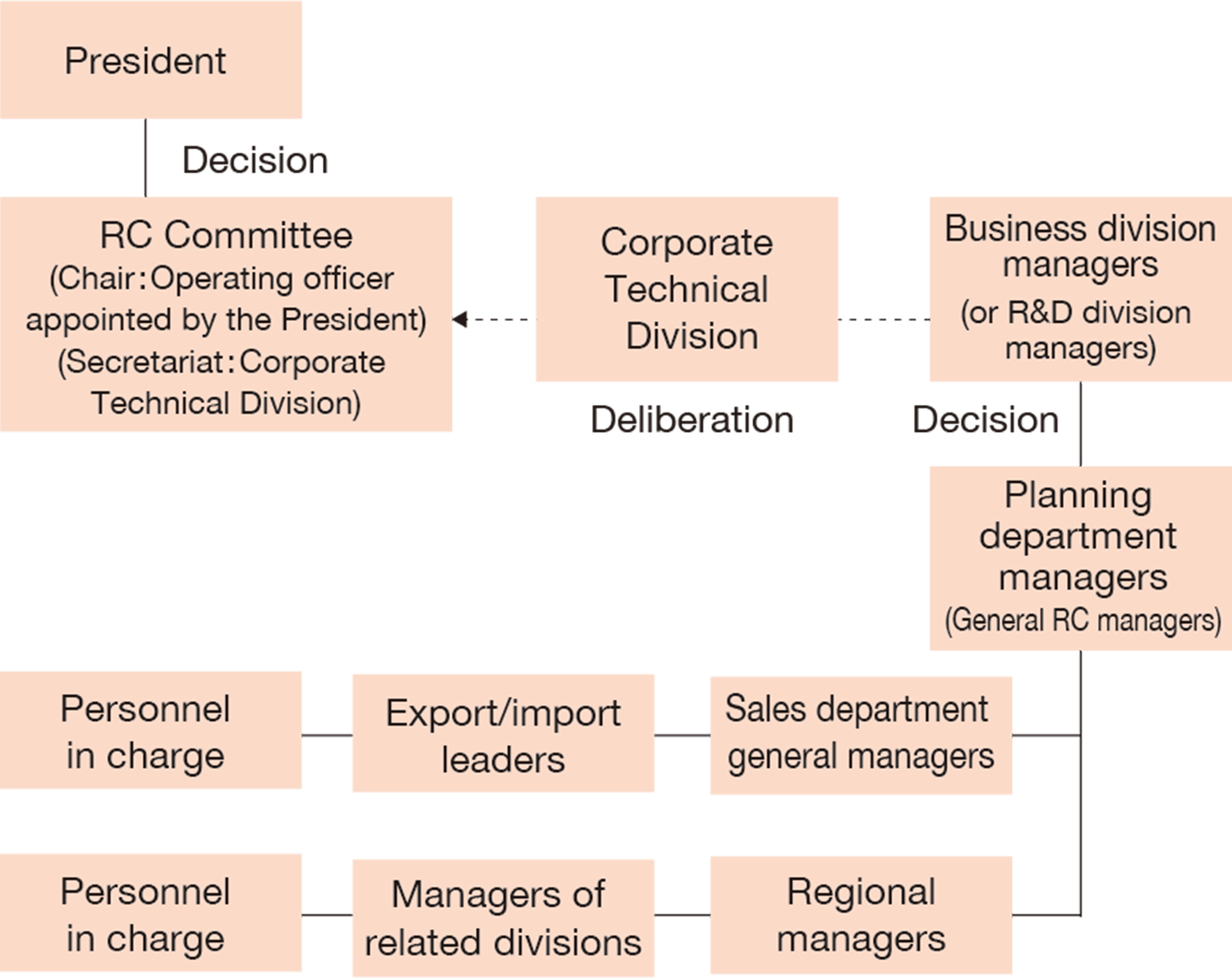
Figure 1. System diagram of production, sales, export, and import of new chemical substances, etc.
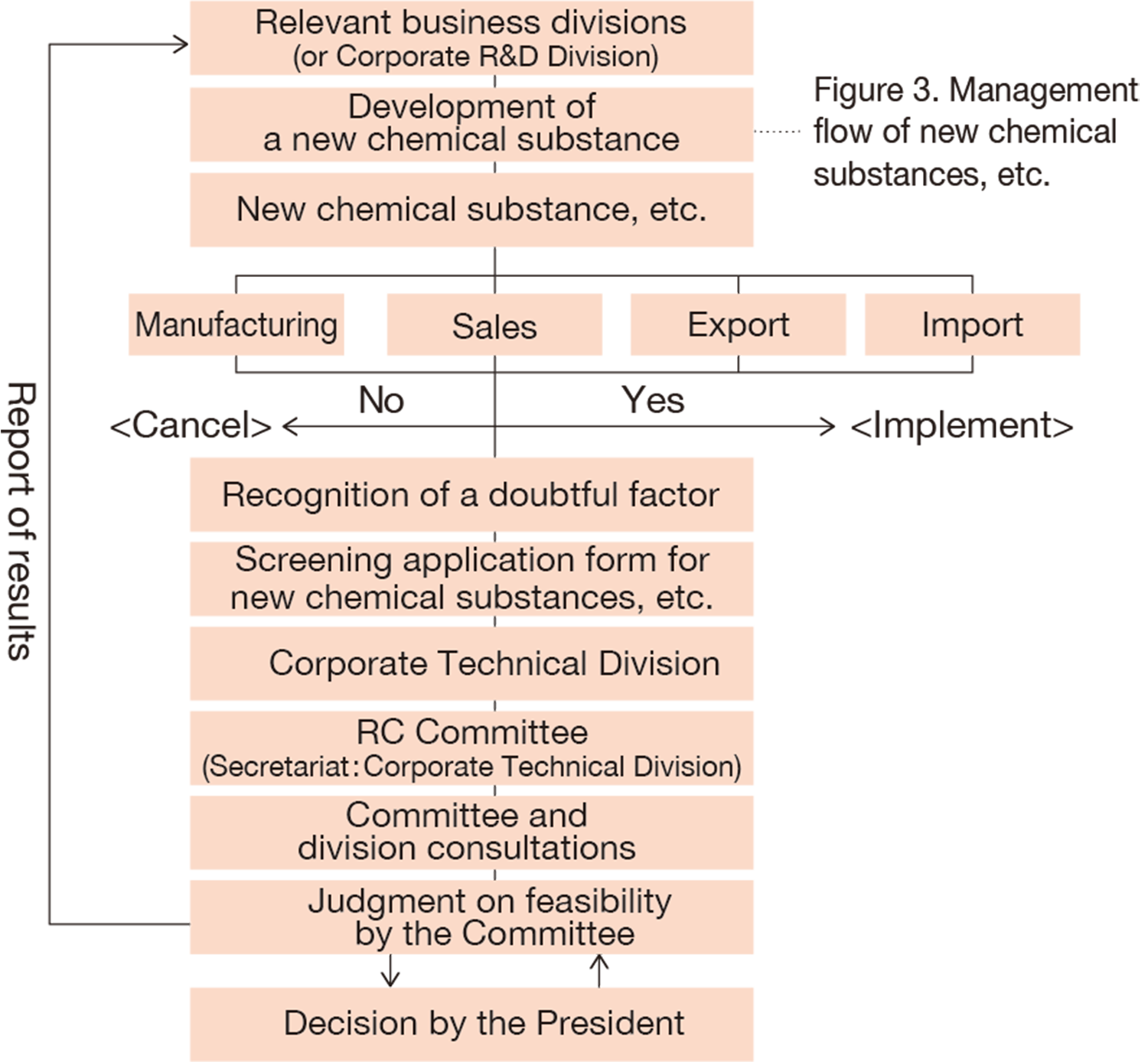
Figure 2. Inspection flow of new chemical substances, etc.
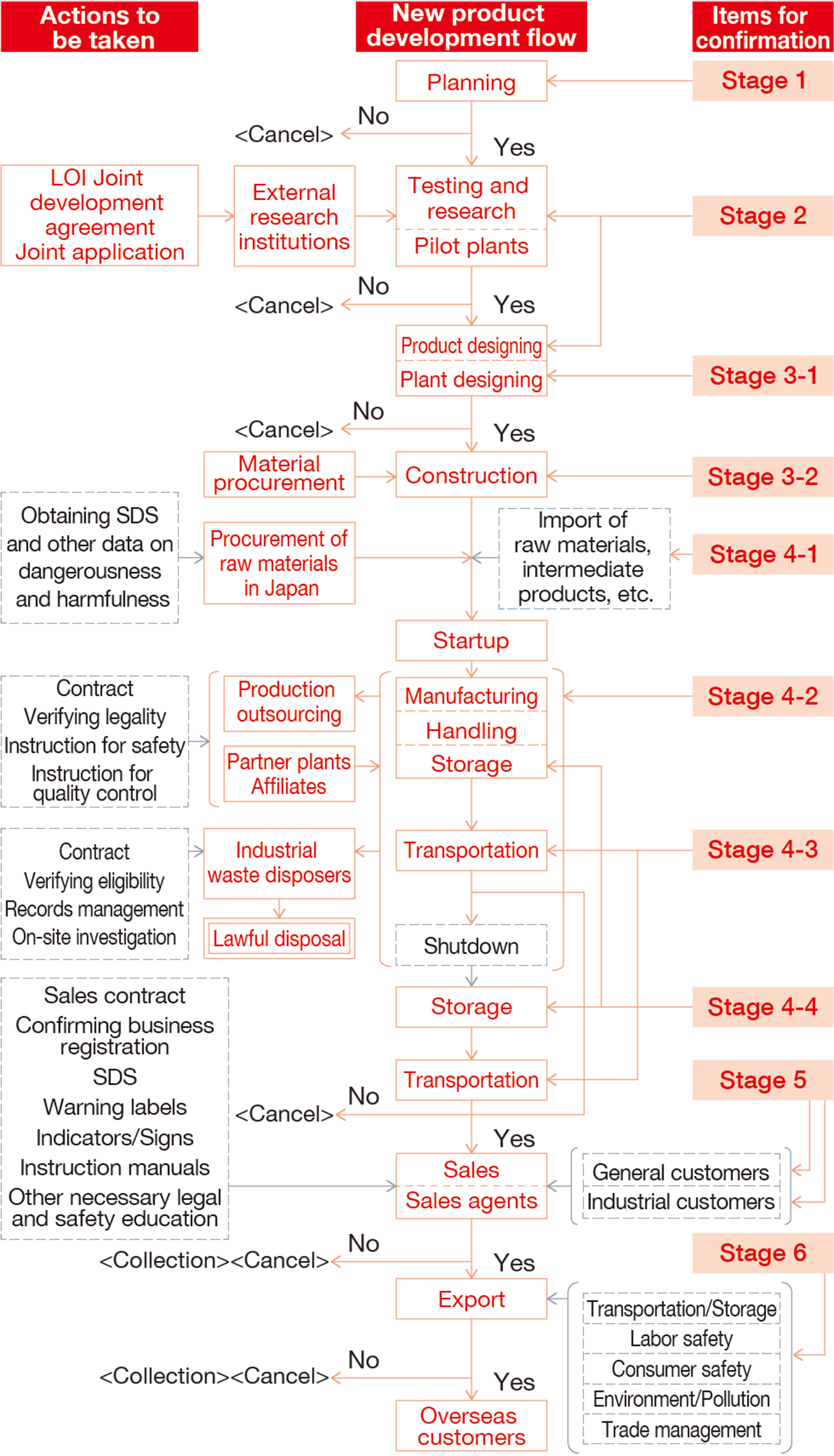
Figure 3. Management flow of new chemical substances, etc.
Items for confirmation in management flow of new chemical substances, etc.
| Stage | Principal items for confirmation |
|---|---|
| 1 | (1) Quality planning (terms of use and impact on the environment, quality of competitors’ products, performance demanded by customers, selling points), (2) Trademark/Patent, Response plan to laws and regulations in Japan and overseas, (3) Development plan (system, schedule, R&D expenses, safety test expenses, etc.), (4) Production plan (production processes, facilities for research and trial experiments), (5) Sales and export plan, (6) Profit and loss plan |
| 2 | (1) Confirmation of the details of marketability and salability (functions, safety, container/package, transportation method, measures against industrial wastes, expenses for production and selling, sales prices, energy saving issues, etc.), (2) Establishment of production processes and analysis/inspection method, (3) Research for the necessity of GLP and GMP, (4) Research for specific value, reactivity, and explosiveness, (5) Confirmation of safety test expenses, etc., (6) Application of new chemical substances (Chemical Substances Control Law and Industrial Safety and Health Act), (7) Research for CAS, TSCA, HCS, CEPA, WHMIS, EINECS, REACH Regulation, FD&C Act, etc., (8) Confirmation of SDS, warning labels, indications and signs, instruction manual, information on each type of toxicity, (9) Sales manual, (10) Contract details, (11) Application for patent and trademark, (12) Retention of documents and records |
| 3-1 | (1) Evaluation of cleaner production (reduction of wastes and prevention of generation), (2) SA on safety and disaster prevention for equipment, processes, and operations (including health problems), (3) Judgment on the effectiveness of the investment |
| 3-2 | (1) Industrial Safety and Health Act, (2) High Pressure Gas Safety Act, (3) Fire Service Act, (4) Explosives Control Act, (5) Act on the Prevention of Disaster in Petroleum Industrial Complexes and Other Petroleum Facilities, (6) Air Pollution Control Act, (7) Ozone Layer Protection Law, (8) Energy Saving related Laws, (9) Water Pollution Prevention Act, (10) Noise Regulation Law and Vibration Regulation Law, (11) Offensive Odor Control Law, (12) Waste Management and Public Cleansing Act, (13) Act on Prevention of Marine Pollution and Maritime Disaster, (14) Building Standards Act, (15) Poisonous and Deleterious Substances Control Act, (16) Act on Securing Quality, Efficacy and Safety of Products Including Pharmaceuticals and Medical Devices, (17) Food Sanitation Act, (18) Chemical Substances Control Law, (19) Agricultural Chemicals Regulation Act, (20) Act on the Regulation of Radioisotopes, etc., (21) Port Regulations Law, (22) Civil Aeronautics Act, (23) Road Transportation Act, (24) Factory Location Act, (25) Municipal ordinances on prevention of fire, pollution, etc. |
| 4-1 | (1) Prior confirmation of the presence of dangerous and harmful substance, (2) Examination of laws and regulations for the relevant substance, (3) Securing sufficient labor for SDS, warning labels, indications and signs, instruction manual, and others |
| 4-2 | (1) Building Standards Act, (2) Fire Service Act, (3) Explosives Control Act, (4) High Pressure Gas Safety Act, (5) Act on the Prevention of Disaster in Petroleum Industrial Complexes and Other Petroleum Facilities, (6) Act on Rationalizing Energy Use, (7) Electricity Business Act and Gas Business Act, (8) JIS, (9) Law for Promotion of Effective Utilization of Resources, (10) Waste Management and Public Cleansing Act, (11) Chemical Substances Control Law, (12) Industrial Safety and Health Act (Article 57-4 Ordinance on Prevention of Organic Solvent Poisoning, Ordinance on Prevention of Dangers Due to Specified Chemical Substances, Ordinance on Prevention of Tetraalkyl Lead Poisoning, Ordinance on Prevention of Lead Poisoning, Ordinance on Prevention of Dangers Due to Dust, Ordinance of Prevention of Ionizing Radiation Dangers), (13) Act on Securing Quality, Efficacy and Safety of Products Including Pharmaceuticals and Medical Devices, (14) Poisonous and Deleterious Substances Control Act, (15) Food Sanitation Act, (16) Agricultural Chemicals Regulation Act, (17) Act on the Regulation of Radioisotopes, etc., (18) Implementation of SA, SOP, and measures for health problems, (19) PM system, (20) QA (ISO 9000 series and JIS Z9900 series, (21) the completion of SDS, warning labels, indications and signs, instruction manual, etc. |
| 4-3 | (1) Explosives Control Act, (2) High Pressure Gas Safety Act, (3) Poisonous and Deleterious Substances Control Act, (4) Fire Service Act, (5) Act on the Regulation of Radioisotopes, etc., (6) Railway Operation Act, (7) Road Transport Vehicle Act, (8) Road Act (underwater tunnel) , (9) Ship Safety Act, (10) Port Regulations Law, (11) Act on Prevention of Marine Pollution and Maritime Disaster, (12) Maritime Traffic Safety Law, (13) Civil Aeronautics Act, (14) Postal Act, (15) Others (carrying documents, qualification, vehicle, container, loading standards, and indications and signs) |
| 4-4 | (1) Confirmation of precautions for indication/sign, (2) Confirmation of precautions for storage |
| 5 | (1) General and industrial customers: distribution of warning labels, indications and signs, and instruction manual, (2) Industrial customers: SDS, quality warranty card, contract, confirmation of business registration, etc. |
| 6 |
|
Initiatives to Improve Information Accuracy in Chemical Substance Management
The NOF Group focuses on sustainable chemical substance management and is working to improve the accuracy of information on the following points.
We introduced a comprehensive chemicals management system and work to ensure reliable operation of the mechanism for providing safety data sheets (SDSs) so that hazard information related to our products is easily available to our customers and employees. Furthermore, by fiscal 2025, we plan to establish a company-wide chemical substance database and enhance the functions of our chemical substance management system.
First, the chemical substance management processes will be digitized to ensure accuracy and rapid access to information.
This ensures strict management of data related to the handling of chemical substances and supports efficient decision-making.
In addition, we are also working to expand the functions of the system to track and manage important information such as usage and handling history of chemical substances, in order to improve transparency and visibility. This allows us to more accurately assess the risks of chemical substances and their impact on the environment, and to help formulate sustainable management strategies.
Furthermore, strengthening partnerships is another important initiative. While building cooperative relationships with suppliers and customers, the NOF Group strives to improve its products through continuous dialogue with customers in order to provide appropriate products in terms of chemical substance management. We also collaborate with industry associations and regulatory bodies and strive to exchange information and expertise. In this way, we aim to contribute to raising the level of chemical substance management throughout the industry and to achieve further development.
Finally, our sustainability initiatives include the promotion of research and development. The NOF Group is focusing on development of chemical substances that are more environmentally friendly.
We aim to provide high-performance products while minimizing negative environmental impact. In this way, we are working to achieve a sustainable business model while meeting the needs of our customers.
The above are the main points on which the NOF Group is working to improve the accuracy of information on chemical substance management.
The NOF Group aims to maintain the trust of its customers and provide valuable returns to all stakeholders while pursuing sustainable management.
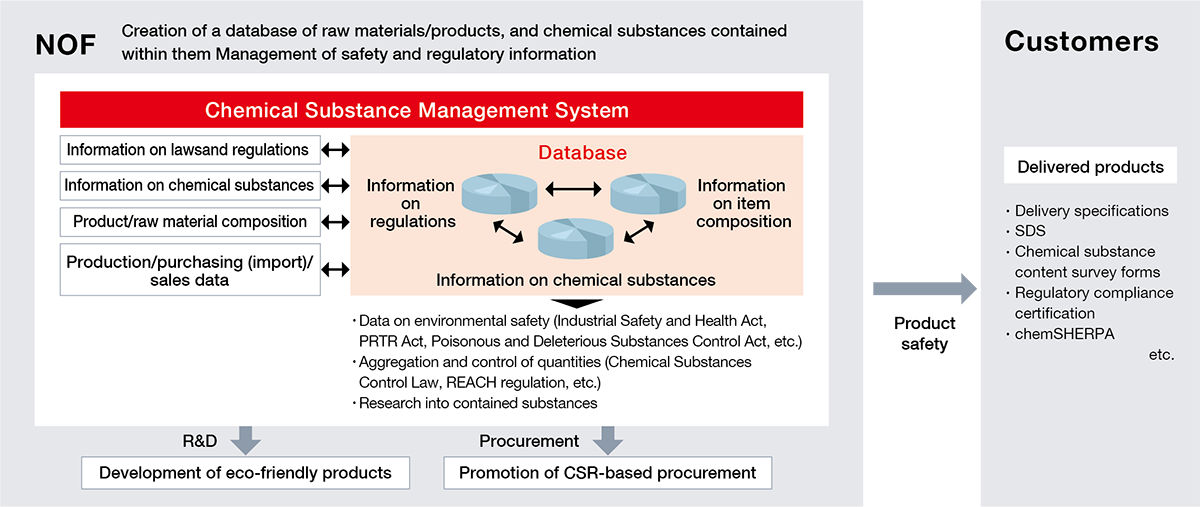
Overview of Chemical Substance Management System
Chemical Substances Risk Assessment
The NOF Group aims to achieve “zero accidents with lost workdays” through efforts to reduce all risks of occupational accidents and prevent their occurrence.
As part of these efforts, in order to prevent occupational accidents caused by chemical substances, the implementation of chemical substance risk assessments based on the Ordinance on Industrial Safety and Health is set as one of the annual RC activity targets related to occupational safety, and is carried out across the NOF Group’s domestic production, R&D, and quality control divisions. During the RC Committee’s regularly held RC audits at each production site, the status of implementation (target implementation rate: 100%) is verified, ensuring a system to reliably and thoroughly address the growing number of chemical substances subject to risk assessments each year.
Initiatives for the Global Framework
Initiatives for the Global Framework on Chemicals (GFC*)
NOF deeply recognizes the importance of the Global Framework on Chemicals (GFC) and is proactively advancing initiatives based on it. The GFC provides international cooperation and guidelines for the management and regulation of chemicals, with the aim of protecting both the environment and human health. Among the various GFC targets, NOF has implemented concrete initiatives particularly addressing B2 (information provision and management) and D1 (resource circulation and greenhouse gas reduction).
Firstly, for the B2 target, NOF utilizes chemSHERPA to provide chemical substance information to downstream users, thereby enhancing transparency and safety across the supply chain. In addition, we have introduced a chemical substance management system that centralizes management of environment- and safety-related data associated with its products, enabling efficient and effective chemical management.
Next, for the D1 target, NOF is promoting the recycling of waste plastics and strengthening its resource recycling initiatives. Through these efforts, we are reducing waste and promoting the effective use of resources. In addition, NOF is working to reduce greenhouse gas emissions by setting and implementing specific goals to contribute to sustainable development.
Going forward, NOF will continue initiatives aligned with the GFC, striving for environmental protection and the realization of a sustainable society.
Wearing Protective Equipment
With the entry into force of the revised Industrial Safety and Health Act in April 2024, not only is it mandatory to appoint a chemical substance control whose duty is to autonomously manage chemical substances, but it is also mandatory for employees who handle chemical substances to wear protective equipment and for a person in charge of protective equipment to select appropriate protective equipment and manage its use. The NOF Group is once again working to ensure the wearing of protective equipment, which it required from before, and has established a management system in line with the revised law.
Transportation Safety
The NOF Group is promoting the reduction of the environmental load in transportation, while at the same time engaging in activities to ensure the safety of products in transport. The Group has always treated transportation safety with desirable care, as it handles a wide range of hazardous materials. In particular, all our employees are working as one to thoroughly implement safety measures with the goal of achieving “zero accidents that adversely affect distribution.” We are also strengthening our management systems to prevent leaks or spills of chemical substances due to an accident.
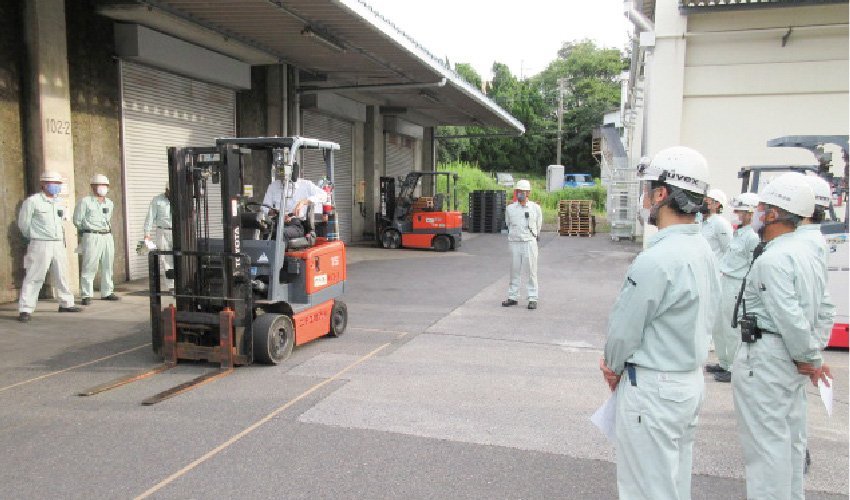

Forklift class (NICHIYU LOGISTICS CO., LTD.)

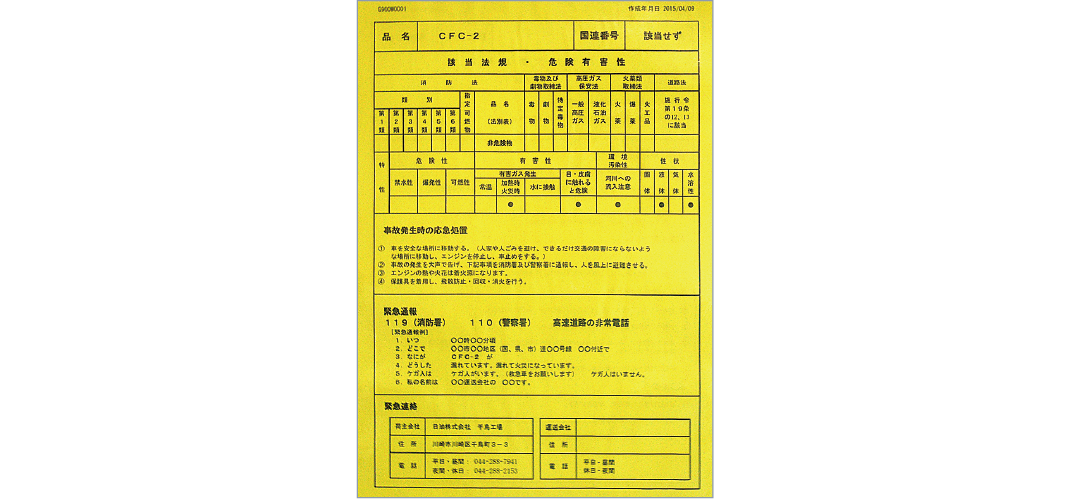
Yellow Cards
Should an accident occur during the transportation of chemical substances, it could have dire consequences on human life, the neighboring area, the cargo, and the road. The Yellow Card states the measures transport operators, the fire brigade, the police, and others should take, as well as contact and notification information, in the event of such an accident. The NOF Group strictly requires that such cards should be provided to transport operators involved, who are also required to carry the card with the corresponding product while in transportation.
By monitoring the operating status of reefer container compressors and their location information, we are creating documentation aimed at improving operational efficiency while enhancing transport safety.
Yellow Cards





