Product information
- TOP
- Business
- Functional Foods
- Health-related Products
- coating-products
Health-related Products
Coatings
The Fats-coating technique that we developed coats powdered active ingredients with fats at room temperature to improve stability, mask the undesired taste, prevent moisture absorption, and prevent direct contact. Many coated products such as vitamins and natural extracts have been put into practical use to meet health needs and applied to the food and animal feed markets.
Recently, we also developed a coating technique using a water-insoluble substance. These techniques can achieve acid resistance and increase bioavailability expanding the scope for coated products.
Product lineup
| Product name | Features | Main application |
|---|---|---|
| VC-80R | Fats-coating product containing 80% L-ascorbic acid | Tablets and stick items |
| VC-90R | Fats-coating product containing 90% L-ascorbic acid | Tablets and stick items |
| ASCORBIC ACID-95R | Fats-coating product containing 95% L-ascorbic acid | Tablets and stick items |
| VB MULTI-COAT | Multi-coating product containing B vitamins based on the daily nutrient requirements of an adult male | Tablets and stick items |
| FP-80R | Fats-coating product containing 80% ferric pyrophosphate | Tablets and stick items |
| BIFIDUS MC-100 | Fats-coating product containing bifidobacteria with pressure resistance (containing 10 billion cells per gram) | Tablets and stick items |
| TABWEL COAT® CARNITINE TARTRATE | Fats-coated L-carnitine L-tartrate with enhanced tableting properties | Tablets and stick items |
| CITRIC ACID MC-80R | Fats-coating product containing 80% citric acid | Tablets and stick items |
Fats-coatings
Fats-coating technique is NOF’s unique technology for coating the surface of active ingredients with fats in powder form.
The characteristics of this technique include:
(1) No heating process and no use of water or solvent. This means the technique is suitable for coating functional ingredients that are sensitive to heat, water and solvent. (e.g., for beneficial bacteria such as lactobacillus and a functional ingredient with a low melting point such as α-lipoic acid).
(2) It can coat individual particles with no sticking between them, so you can make products coated in fine powders.
(3) You can set the amount of coating agent, meaning the coating coverage, to a desired thickness to allow controlled release.
Conceptual diagram showing fats-coating
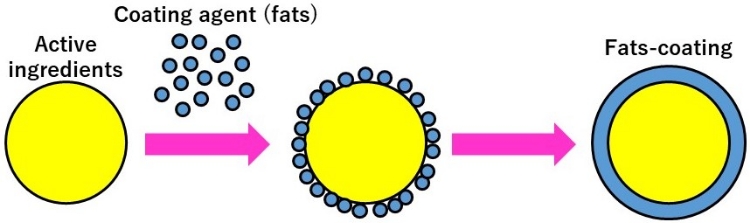
Features
- No water or solvent is used
- No heating process
- Can coat individual particles
Multi-coating
Multi-coating is a combination of the granulation-coating technique and the abovementioned fats-coating technique. The granulation-coating technique coats powder particles while granulating them using a water-soluble or sparingly water-soluble granulating film.
Compared to fats-coating alone, this combination results in much higher coating capabilities. The features of the multi-coating technique are:
(1) You can coat even fine powder, and
(2) You can add granulation film with different features to obtain capsules with new functions (e.g., acid resistance).
Conceptual diagram showing multi-coating
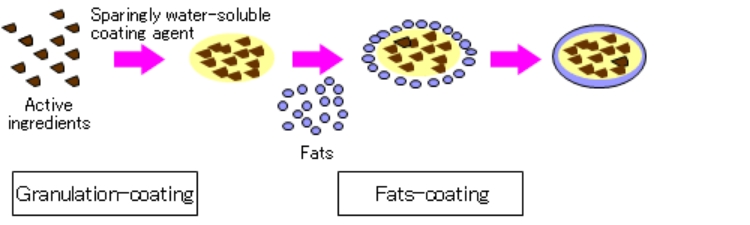
Features
- Even fine powder can be coated
- The coating effect improves
- You can get acid resistance
Effects added by coating
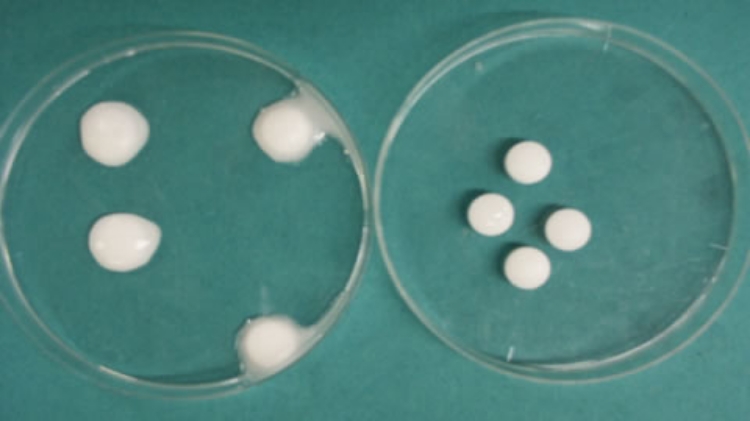
1. Prevents moisture absorption
Preservation test on granules containing xylo-oligosaccharide
(40°C; 75% Rh; 24-hour preservation)
2. Delaying of darkening
Preservation test on royal jelly powder (40°75% Rh; 2-week preservation)

[center image]10% Fats coated royal jelly powder
[Right image] 20% Fats coated royal jelly powder
3. Sustained release
Can control the dissolution behavior by the quantity of fats used as coating
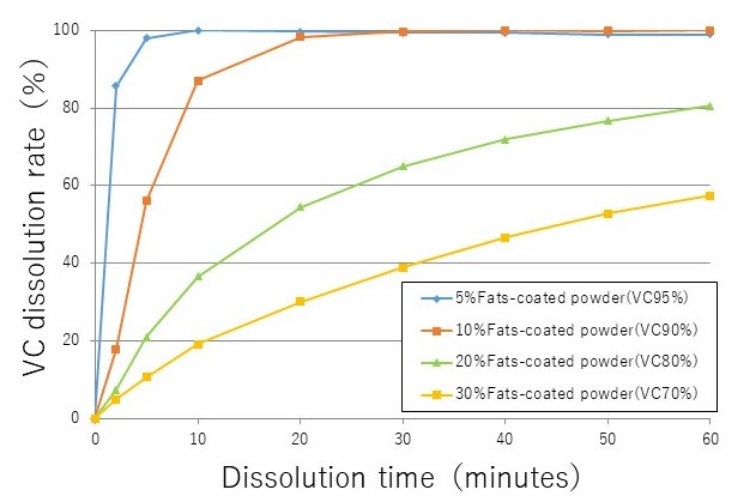
(Test solution: purified water; temperature: 37°C; stirring rate: 100 rpm)
4. Increasing bioavailability
Comparison between absorption into the body between products containing non-coated vitamin B2 and coated vitamin B2
(Product intake 60 mg as vitamin B2, followed by measurement of the vitamin B2 level in blood 24 hours later)
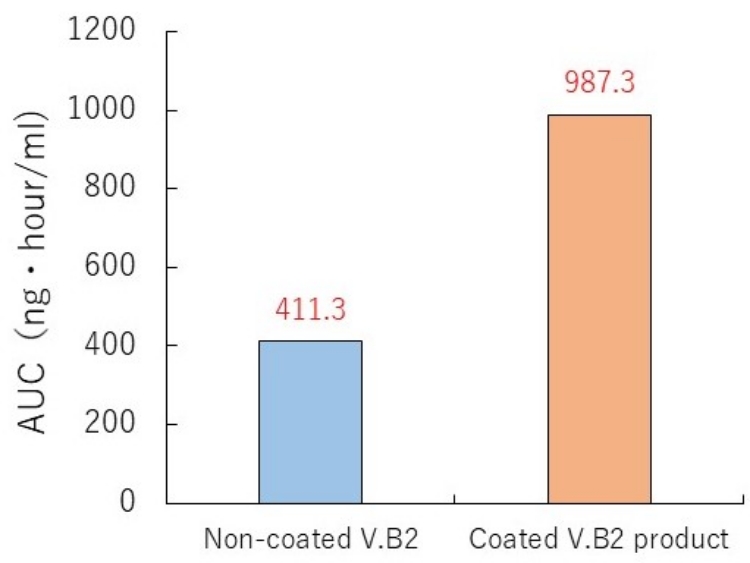
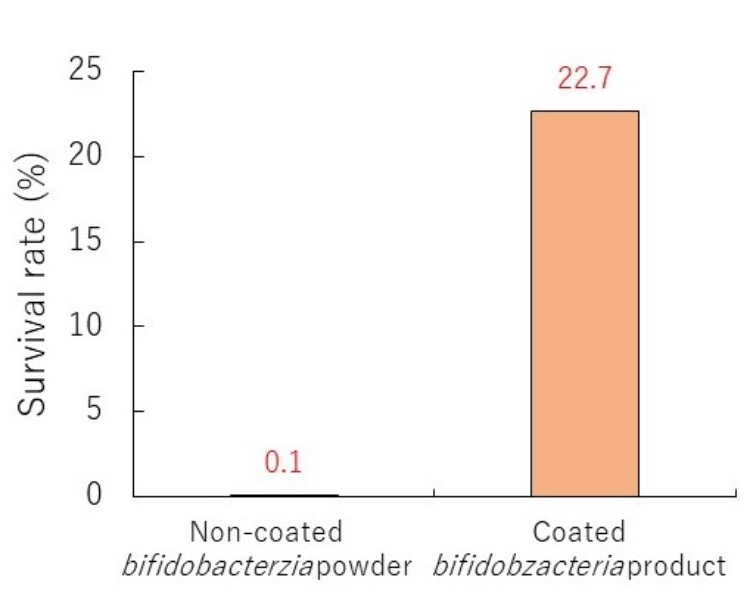
5. Improving acid resistance
Enhanced bifidobacteria survival rate under acidic conditions
Acid resistance test (pH3.0; 37°C; 200 rpm; 60 minutes)
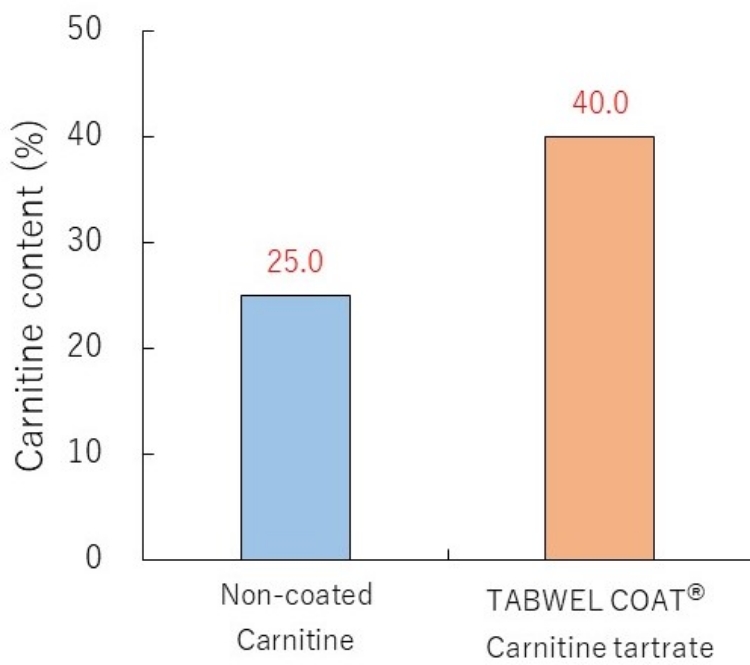
6. Higher ingredient content in a tablet
Increasing the ingredient content in a tablet
Assuming a carnitine intake of 500 mg a day and a tablet is 300 mg, the number of tablets to be taken a day can be reduced from 6 or 7 tablets made with non-coated carnitine to 4 tablets made with coated carnitine.