Product information
- TOP
- Business
- Life Science
- Medical devices products
Medical devices products
Coating Materials for Medical Device
Products
| Product name | Solubility | substrate | Glass | SUS | Silicone | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PE | PS | PP | PU | PC | PEEK | PET | |||||
| LIPIDURE®-CM5206 | Ethanol-soluble Water-insoluble |
○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | - | ○ | ○ | ○ | NA |
| Can be used by dissolved in ethanol. Results of safety tests are shown in Table 1. |
|||||||||||
| LIPIDURE®-CR2001 | Ethanol-soluble Water-soluble |
○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | - | ○ | ○ | - | - | NA |
| Can be chemically bonded to the base material surface by photoreaction. | |||||||||||
| LIPIDURE®-CR3001 | Ethanol-soluble Water-soluble |
○* | ○* | ○* | - | ○* | - | ○* | ○* | ○* | ○* |
| Can be used for hydrophilic coating on the metals and silicone rubber. * Pretreatment is necessary. |
|||||||||||
| LIPIDURE®-NH01 | Water-soluble | Reactive polymer that has amino group | |||||||||
| Can react with functional groups (such as carboxyl group) on the base material surface. | |||||||||||
○:Applicable, NA:Not available, - :Not tested
Table 1 Results of safety tests for LIPIDURE®-CM5206
| Study item | Results |
|---|---|
| Cytotoxicity study (ISO10993-5) | Negative |
| Irritation and Test Sensitization study (ISO10993-10) | Negative |
| Acute Systemic Toxicity study (ISO10993-11) | Negative |
| Hemolysis study (ISO10993-4) | Non hemolytic |
| Intracutaneous study (ISO10993-10) | Negative |
| Bacterial Reverse Mutation study (ISO10993-3) | Negative |
Index
- Features of medical device coating materials
Features of medical device coating materials
Suppression of protein adsorption
Coating a product with LIPIDURE® prevents protein from being adsorbed onto the surface of the base material.

[Test procedure]
A 96-well polystyrene plate was coated with LIPIDURE®-CM5206 and HRP-IgG conjugate solution (diluted 25,000-fold by PBS) was added into each well. After one hour of incubation at 25°C, each well was washed four times with PBS containing 0.05% Tween20. Tetramethylbenzidine (TMBZ) solution (substrate solution of HRP) was added to each well and incubated for 10 minutes at 25°C. After stopping the reaction, the HRP amount adsorbed was compared by measuring the absorbence at 450 nm.
Suppression of cell adhesion
Coating a product with LIPIDURE® prevents cell lines from adhering to the surface of the base material.
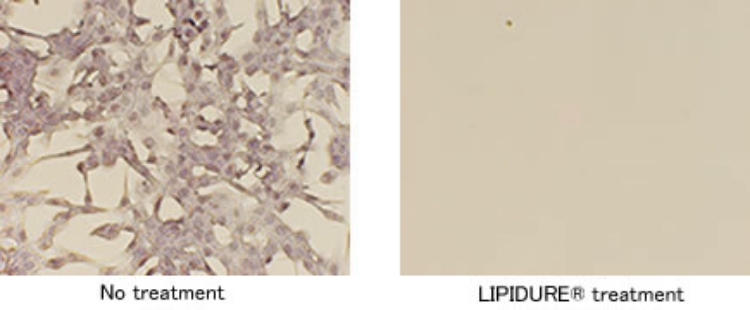
[Test procedure]
A 384-well polystyrene plate was coated with LIPIDURE®-CM5206 and suspensions of NIH3T3 cell (containing 10% CS, DMEM medium) were added into each well(1 × 104 cells/well). After 18 hours of incubation in a CO2 incubator, the medium was removed. 50 µL of hematoxylin solution was added to each well and incubated for 10 minutes to stain the cell nucleus. After washing the plate with purified water and drying it, each well was observed using microscope.
Floating culture and formation of spheroid (cell aggregate)
Coating the cell culture vessel with LIPIDURE® prevents cells from adhering to the surface of the vessel and makes floating culture possible. Formation of spheroid (cell aggregate) and formation of embryoid body of ES cells and iPS cells are also possible.

[Test procedure]
A 96-well polystyrene plate (round bottom) was coated with LIPIDURE®-CM5206 and HeLa, HepG2 or human mesenchymal stem cells were seeded into each well. After 48 to 72 hours of incubation in a CO2 incubator, a phase-contrasted microscope was used to observe the plate.
Suppression of macrophage adhesion
Coating with LIPIDURE® prevents macrophage from adhering to the surface of the base material.
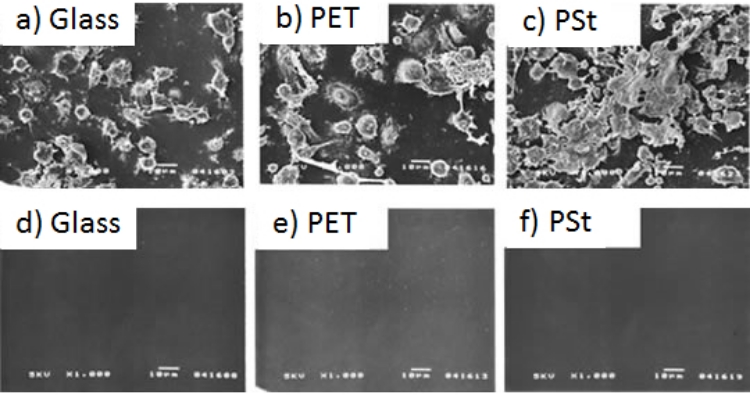
a) to c): No treatment
d) to f): LIPIDURE® treatment
[Test procedure]
Mice were injected intraperitoneally with thioglycolate medium for macrophage induction. Macrophage was extracted from the abdominal cavity four days after induction and adjusted to a concentration of 6.25 × 105 cells/mL. 500 µL/well of solution was then injected to a 24-well plate. Different samples (glass, polyester, polystyrene) were added to the well and left to interact for one hour. The samples were washed with a buffer solution and fixed with 2.5 wt% of glutaraldehyde solution. The gold deposited from the sample was observed using scanning electron microscope (SEM).
Highly-lubricious Coating
LIPIDURE® has high affinity for water. Coating the surface of the base material with LIPIDURE® can reduce the friction coefficient.
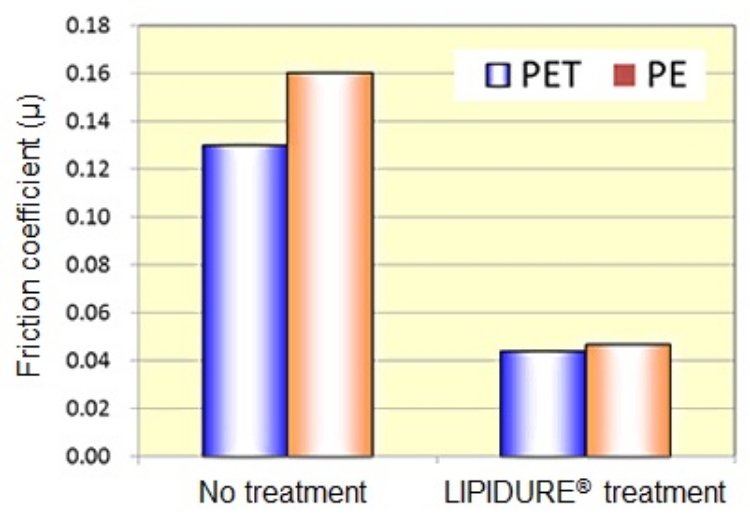
[Test procedure]
LIPIDURE®-CM5206 was dissolved in ethanol and PET and PE substrate plates were dipped in the solution for ten seconds and dried at 50°C for over three hours. The friction coefficient in the saline was measured using a device to measure surface physical properties.
References
K. Ishihara, T. Ueda, N. Nakabayashi et al. (1990) Polym.J. Res.22, 355-360.
K. Ishihara, N. Nakabayashi et al. (1990) J. Biomed.Mater.Res.24, 1069-1077.
K. Ishihara, N. Nakabayashi et al. (1994) J. Biomed.Mater.Res.28, 1347-1355.
K. Ishihara, N. Nakabayashi et al. (1998) J. Biomed.Mater.Res.39, 323-330.
K. Ishihara, N. Nakabayashi et al. (2003) J. Biomed.Mater.Res.64, 411-416.
Coating method for LIPIDURE®-CM5206
Method for coating the surface of the base material with LIPIDURE®
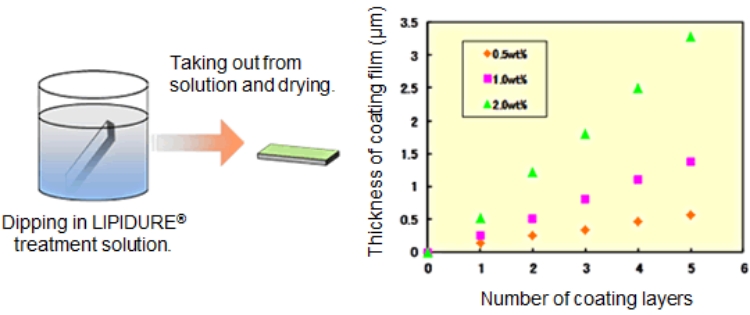
1. Immersion (Dipping) method
Dip a substrate in polymer solution and take it out after three to five minutes and dry it.
Coating the plate with 0.5 wt% of LIPIDURE®-CM5206 solution in ethanol will create a film of about 100 nm in thickness each time. The thickness of the coating film will increase with additional layers. Alternatively, coating with a higher concentration of the LIPIDURE®-CM5206 solution can increase the thickness of the coating film (refer to following figure).
2. Casting method
Place the polymer solution on the substrate and dry it. Slow drying reduces the difference in the thickness of the film.