Using Fats-coating can produce various beneficial effects.
| Protects the active ingredients from the external environment. | |
|---|---|
| Enclosure of materials | |
| Helps to control dissolution of ingredients |
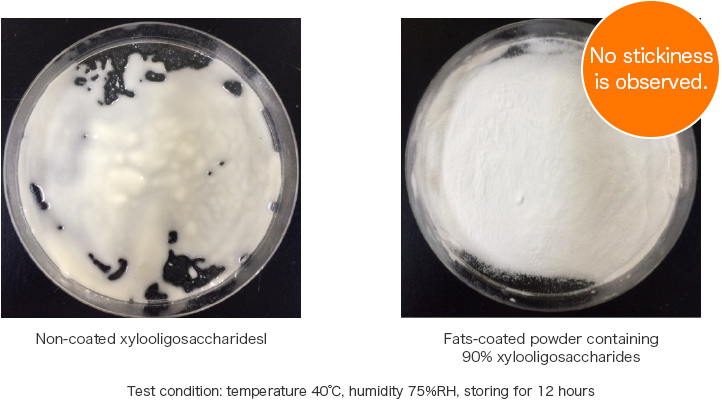
Fats-coating prevents moisture absorption and preserves fluidity. You can apply it to active ingredients with poor handling properties due to its high hygroscopicity.
(Example) Inhibiting hygroscopicity of xylooligosaccharides

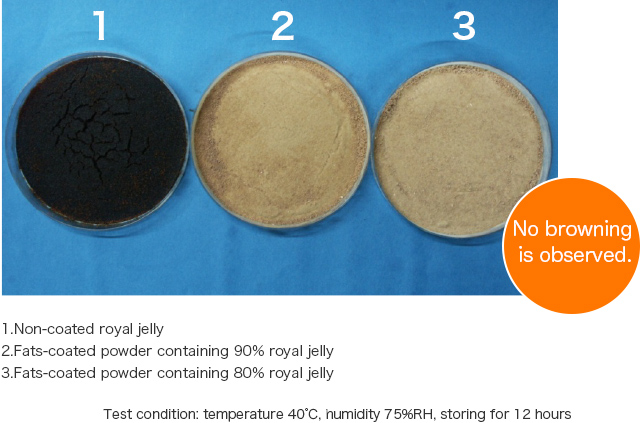
Fats-coating can delay browning reaction by inhibiting the Maillard reaction. That way, you can design formulations without worrying about color changes.
(Example) Delaying browning of royal jelly

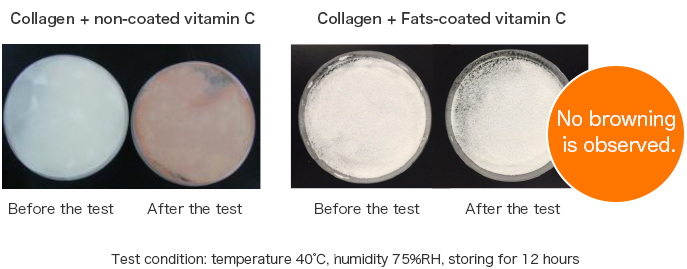
Coating active ingredients with Fats-coating inhibits reactions caused by ingredients contacting one another.
It can inhibit reactions such as the browning reaction resulting from contact between vitamin C and collagen, and the foaming reaction when sodium bicarbonate contacts organic acids.
(Example) Inhibiting the reaction of vitamin C with collagen
(Example) Inhibiting the reaction of sodium bicarbonate with citric acids

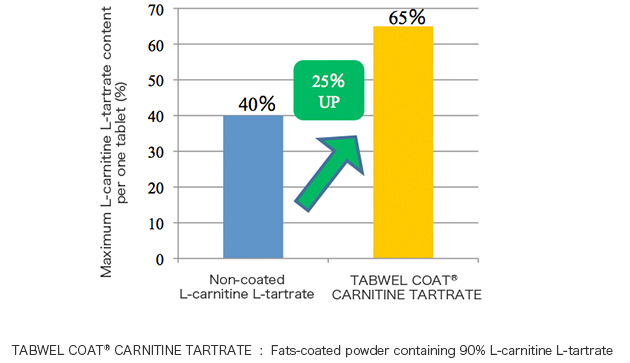
TABWEL® coating process is specially designed to enhance tableting potential by making it easier to compress ingredients that are difficult to compress.
Improved tableting capability makes it possible for a tablet to contain more ingredients, making it possible to reduce the number of tablets that people need to take daily and to design smaller tablets compared to cases of using non-coated powder.
Can form tablets that are easy to swallow and absorb.
(Example) Improved tableting capability of L-carnitine L-tartrate
Fats-coating can prevent the depletion of active ingredients, including vitamins. It offers some advantages, such as eliminating both the need to prepare additional amounts of active ingredients to take into account their depletion during processing and the need to indicate the content range of such ingredients.
(Example) Inhibiting depletion of vitamin B12 and vitamin D3 in multi-vitamin & -mineral tablets
| Initial value | accelerated test period of 4 months (corresponding to 2 years at normal temperatures) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Non-coated powder | Multi-coating products | ||
| vitamin B12 | 2μg (100%) |
1.04μg (52%) |
1.7μg (85%) |
| vitamin D3 | 5μg (100%) |
2.55μg (51%) |
4.1μg (82%) |
* accelerated test conditions: temperature 40℃, humidity 75%RH, packing in aluminum bag
Multi-coating prevents the loss of active ingredients due to tableting pressure, acids, etc.
For example, this coating helps to safely deliver Bifidobacteria, which are known to be highly sensitive to pressure and easily damaged by acids, to the intestines because it can reduce damage caused by tableting pressure and gastric acid.
|
(Example) Using multi-coating to improve the tableting pressure resistance of Bifidobacteria
|
(Example) Using multi-coating to improve acid resistance of Bifidobacteria
|
Using Fats-coating can mask bitterness, saltiness, spiciness and astringency, etc. Fats-coating will make it possible to use ingredients once rejected due to unfavorable flavors.

Fats-coating can prevent volatile ingredients from escaping, helping foods to retain their delicious flavor for long periods.

Fats-coating can delay the dissolution of ingredients to control the timing of the dissolution according to the purpose.
Fats-coated vitamin C products dissolution test data (in vitro)
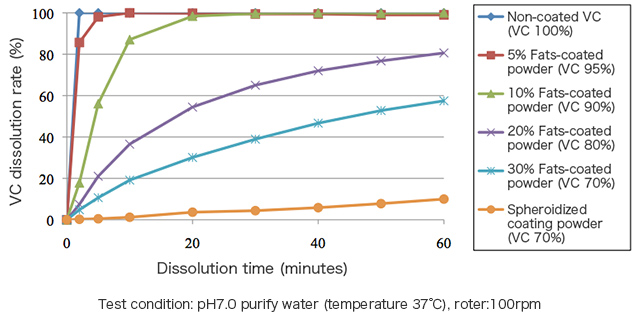
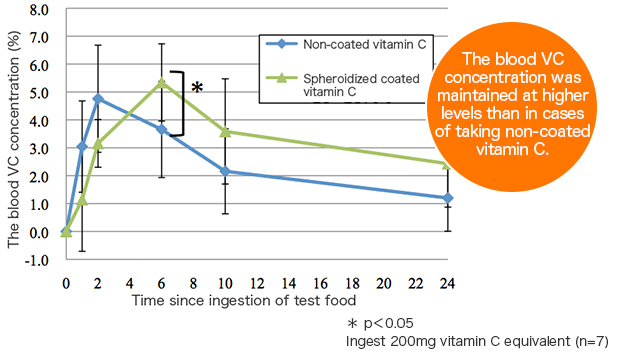
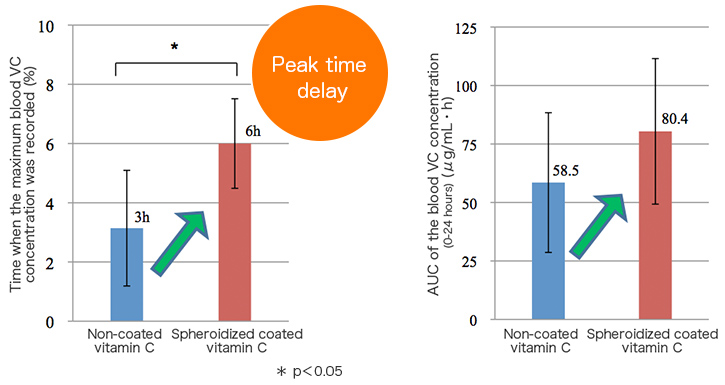
Sustained release of Fats-coated vitamin C products has been also confirmed in human clinical testing.
Change in blood vitamin C (VC) level when taking Fats-coated vitamin C products